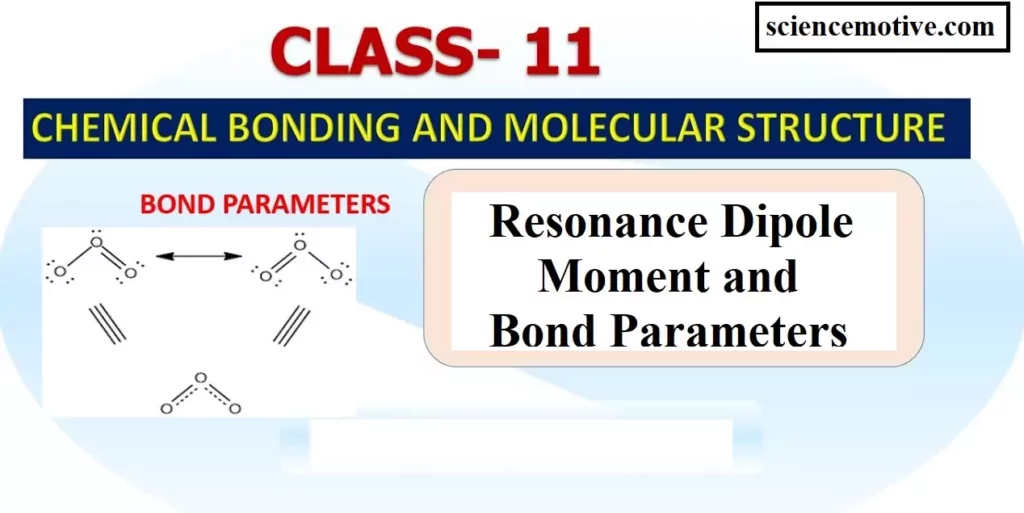
Resonance Dipole Moment and Bond Parameters Resonance Dipole Moment and Bond Parameters: Covalent Bond Parameters: (1) Bond Length: It is defined as the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. It is measured by spectroscopic, X-ray diffraction, and electron diffraction techniques. It is expressed in pico-meter (pm) or in the angstrom unit (A0). Bond lengths depend upon the relative sizes of the atoms. For example, the bond lengths of hydrogen halides follow the sequence H – F < H – Cl < H – Br < H – I because the size of the halogens increases…
Author: Dr. Vikas Jasrotia
Assertion Reason MCQs and Solved Questions Surface Chemistry Assertion Reason MCQs and Solved Questions Surface Chemistry Que 1. What is the sign of ΔH and ΔS for the adsorption of bromine on charcoal? Ans 1. Both ΔH and ΔS are negative. Que 2. Why are substances like platinum and palladium often used for carrying out electrolysis of aqueous solutions? Ans 2. Platinum and palladium are inert materials & are not attacked by the ions of the electrolyte or the products of electrolysis therefore used as electrodes for carrying out the electrolysis. Que 3. Why does physisorption decrease with the increase…
Properties and Applications of Colloids Properties of Colloids (i) Heterogeneous nature: Colloids are heterogeneous in nature and consists of two phases, the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium. (ii) Visibility: The particles are too small to be seen with the naked eye but become visible when viewed through an ultra-microscope due to the scattering of light by them. (iii) Surface tension and Viscosity: The surface tension and viscosity of lyophobic sols are not very different from that of the dispersed medium. But, lyophilic sols show higher viscosity and lower surface tension in comparison to the dispersion medium. (iv) Tyndall Effect:…
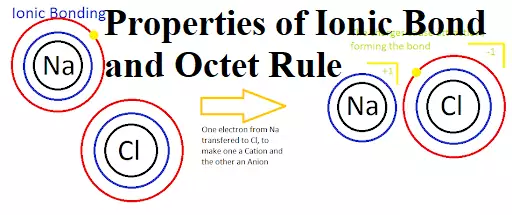
Properties of Ionic Bond and Octet Rule Properties of Ionic Bond and Octet Rule It is observed that the atoms of all the elements, except those for noble gases, tend to remain in a combined state with the atoms of the same or other elements. They do not exist as single atoms under ordinary conditions. Such atomic aggregates occur as molecules. The attractive force that binds the atoms together in a molecule is called a chemical bond. It is formed either by the transfer of electrons or by the sharing of electrons. The elements with one, two, three, four, five,…
Solved Questions Basic Concepts of Chemistry Solved Questions Basic Concepts of Chemistry Que 1. How many significant figures are there in (i) 3.070 and (ii) 0.0025? Ans 1. (i) 4 (ii) 2 Que 2. How many significant figures are present in the answer of the following calculation: .0125 + 0.8250 + 0.025 Ans 2. 0.86 Que 3. The density of vanadium is 5.96 g cm3. Express this in the SI unit. Ans 3. 5960 kg m3 Que 4. The body temperature of a normal healthy person is 370C. Calculate its value in 0F. Ans 4. We know 0F =…
The Colloidal State Preparation and Purification A colloid is an intermediate state between true solution and suspension. In a true solution, the size of the particles is < 1nm. The particles do not settle down under the influence of gravity or by any method and they cannot be filtered by a filter paper. Colloids are heterogeneous systems containing two phases – the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium. Dispersed Phase: The phase which is dispersed in the other (medium) is called the Dispersed Phase or internal phase, or discontinuous phase. Dispersion Medium: The phase or medium in which the dispersion…
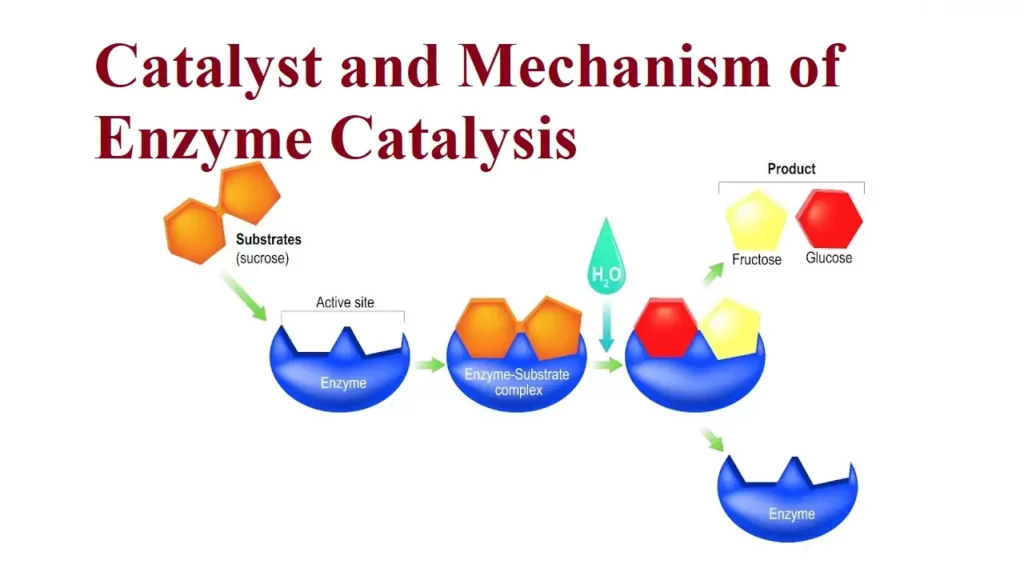
Catalyst and Mechanism of Enzyme Catalysis Catalysis: A catalyst is a substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any permanent chemical change by itself. The process of changing the rate of a chemical reaction by a catalyst is known as Catalysis. Eg:- 2KClO3 + MnO2 → 2KCl+ 3O 473-633k Promoters and Poisons: Promoters are substances that enhance the activity of a catalyst while poisons decrease the…
Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes Atoms and Molecules: Atom is the smallest particle of an element. Molecules are the smallest particle of a substance. A molecule has all the properties of that substance. Types of molecules Based on the type of atoms, there are two types of molecules – The homonuclear molecule and the Heteronuclear molecule. A molecule containing only one type of atom is called a Homonuclear molecule. e.g. H2, O2, N2, O3 (ozone), etc Heteronuclear molecules contain different types of atoms. E.g. CO2, H2O, C6H12O6, NH3, etc. Based on the no. of atoms…
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes Chemistry is the branch of science that deals with the properties, structure, and composition of matter. There are a large number of branches for Chemistry. Some of them are: Inorganic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Physical Chemistry Analytical Chemistry Polymer Chemistry Biochemistry Medicinal Chemistry Industrial Chemistry Hydrochemistry Electrochemistry Green Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes Matter: Matter is anything that occupies space, has a definite mass, and can be perceived by any of our sense organs. Based on the physical state we can divide matter into different categories. Solid-State …
Adsorption and Applications Surface Chemistry Surface Chemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the study of the phenomenon occurring at the surface than bulk. Adsorption: The accumulation of molecular species at the surface rather than in the bulk of a solid or liquid is termed as adsorption. Adsorbate: The substance which is adsorbed is called adsorbate. Adsorbent: The substance whose surface on which adsorption takes place is called adsorbent. The commonly used adsorbents are charcoal, silica gel, alumina gel, clay, colloids, metals in a finely divided state, etc. Adsorption is a surface phenomenon. Some examples of adsorption are:…