MCQs Solved Chemical Kinetics MCQs Solved Chemical Kinetics: Que 1. The rate constant of a reaction is 0.005molL–1s–1. What is the order of this reaction? Ans 1. Zero-order reaction. Que 2. In a reaction, 2A → Products, the concentration of A decreases from 0.5mol L–1 to 0.4 mol L–1 in 10 minutes. Calculate the rate during this interval? Ans 2: Rate = – change in conc. of A/2 x time interval = – [0.4‐0.5]/2×10 = 0.005 mol L–1min–1 Que3. The rate constant for a first-order reaction is 60 s–1. How much time will it take to reduce the…
Author: Dr. Vikas Jasrotia
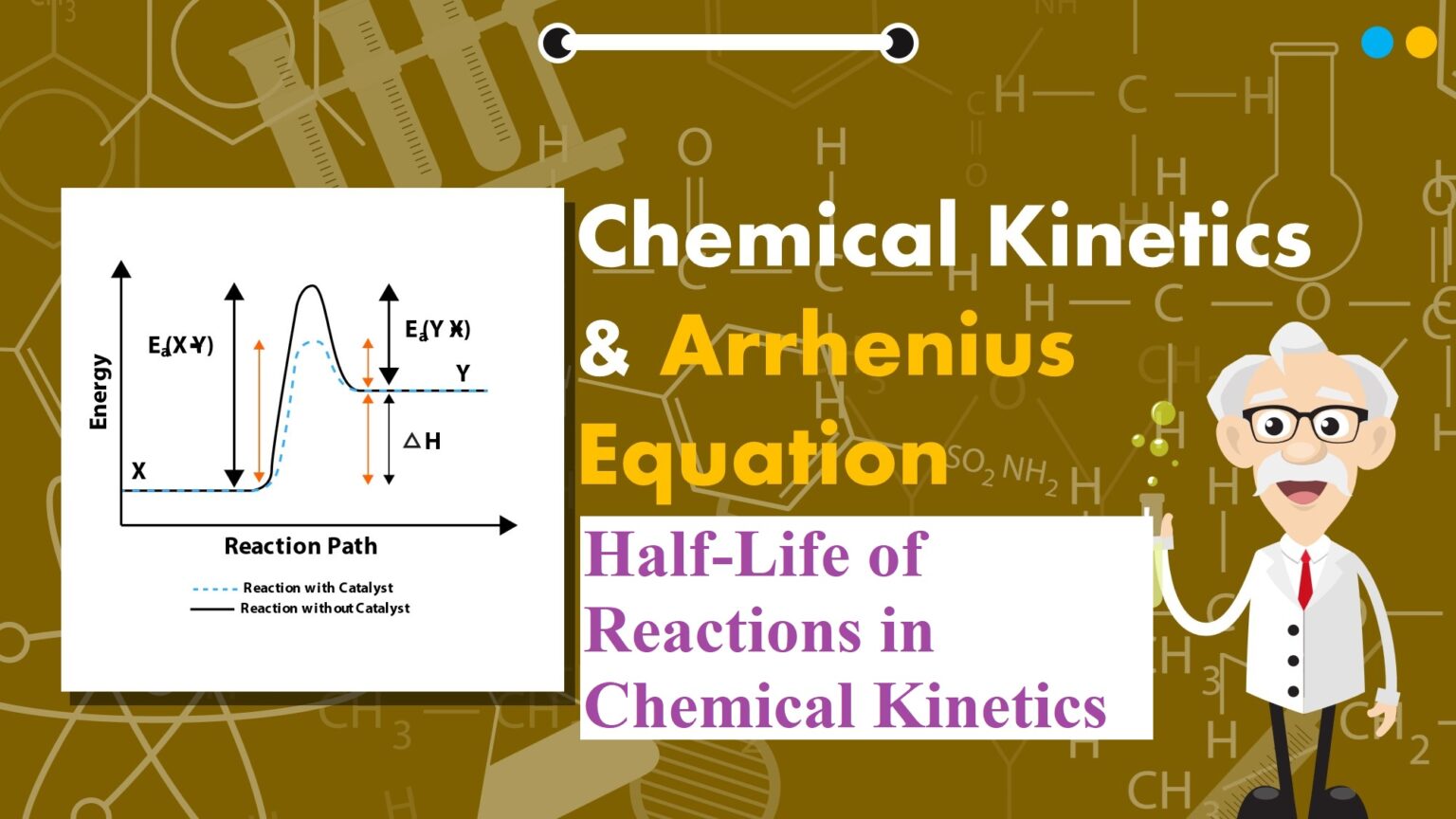
Half-Life of Reactions in Chemical Kinetics Half-Life of Reactions in Chemical Kinetics: Pseudo First Order Reaction: The reactions which are not truly of first order but become reactions of first-order under certain conditions are called pseudo first-order reactions. For example, Hydrolysis of ester (H+). CH3COOC2H5 + H2O → CH3COOH + C2H5OH Rate = k [CH3COOC2H5] [H2O] Since water is in excess and [H2O] is constant, so Rate = k[CH3COOC2H5], Where k = k’[H2O] Inversion of cane sugar (in acid) C12H22O11 + H2O → C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 Cane sugar …
Chemical Kinetics Rate and Order Notes Chemical Kinetics Rate and Order Notes: Chemical Kinetics: The branch of Chemistry that deals with the rate of chemical reaction, factors affecting the rate, and the mechanism of a reaction. Types of Reactions: On the basis of rates (i) Very fast reactions – e.g. precipitation of AgCl (ii) Very slow reactions – e.g. rusting of iron (iii) Reactions taking place at moderate speeds – e.g. hydrolysis of starch Rate of Chemical Reaction: It is the change in concentration of reactant or product with respect to time. OR It is the rate of decrease in…
Solved Questions Electrochemistry Solved Questions Electrochemistry: Que 1. How much electricity in terms of Faraday is required to produce 100g of Ca from molten CaCl2? Ans 1. 5F Que 2. Name the solid substance produced, during the discharge of lead- storage battery. Ans 2. Lead sulphate Que 3. If 0.5 ampere current flows through a wire for 2 hours. Calculate the number of electrons through the wire. …
Primary Secondary Batteries and Corrosion Batteries: A battery is basically a galvanic cell in which the chemical energy of a redox reaction is converted to electrical energy. They are of mainly 2 types – primary batteries and secondary batteries. Primary batteries: Here the reaction occurs only once and after use over a period of time, they become dead and cannot be reused. E.g. Dry cell, mercury button cell, etc. (Primary cells cannot be recharged and reused). (i) Dry Cell (ii) Mercury Cell Primary Secondary Batteries and Corrosion Secondary cells: A secondary cell can be recharged and reused again and again. Here…
Solved MCQs Periodic Classification Solved MCQs Periodic Classification: Q1. Which of the following processes involves the absorption of energy? a) Cl + e- → Cl- b) O- + e‑ → O2- c) O + e- → O- d) S + e- → S- Ans 1. b) O- + e‑ → O2- As the electron is being added to the anion, whereas in all rest of three, the electron is being added to a –neutral atom which will not have as much repulsion as in the case of O-. Q2. Electronic Configuration of most electro negative element is a) 1s2…
NEET JEE Solved Questions Solid State NEET JEE Solved Questions Solid State: Q1. The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. Which of the following statement is/are true about them [AIIMS 1991] (a) Gases and liquids have viscosity as a common property…
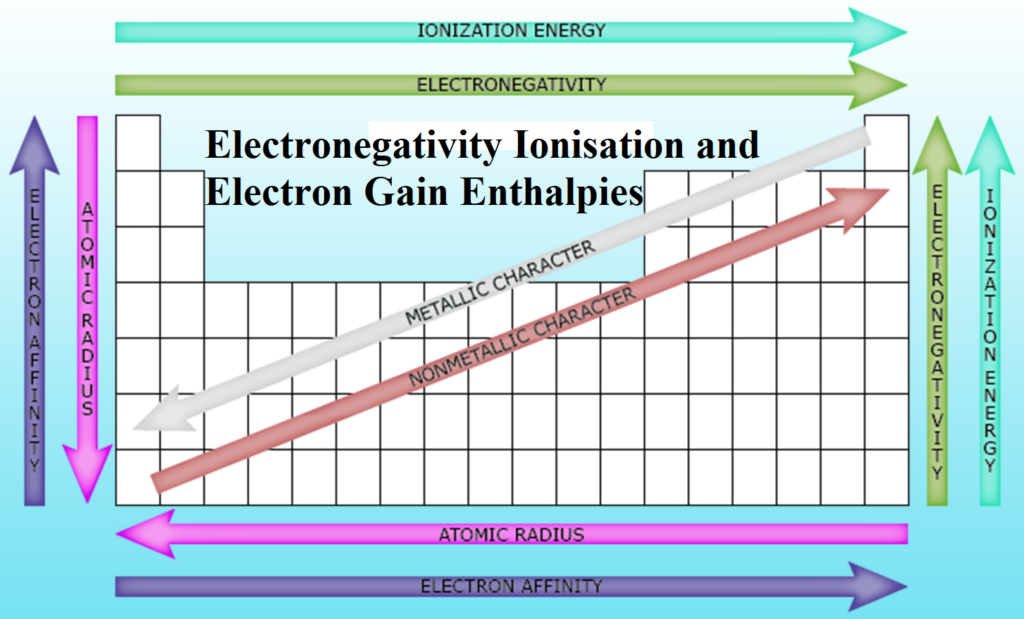
Electronegativity Ionisation and Electron Gain Enthalpies Electronegativity Ionisation and Electron Gain Enthalpies: Ionization Enthalpy (∆iH): Minimum amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound valence electron from an isolated gaseous atom so as to convert it into gaseous cation. It may be represented as: X(g) + ∆iH → X+(g) + e– Its unit is kJ/mol or J/mol. The energy required to remove the first electron from the outermost shell of a neutral atom is called first ionization enthalpy (∆iH1) X(g) + ∆iH1 → X+(g) + e– Second Ionisation enthalpy (∆iH2) is the amount of energy required to remove…
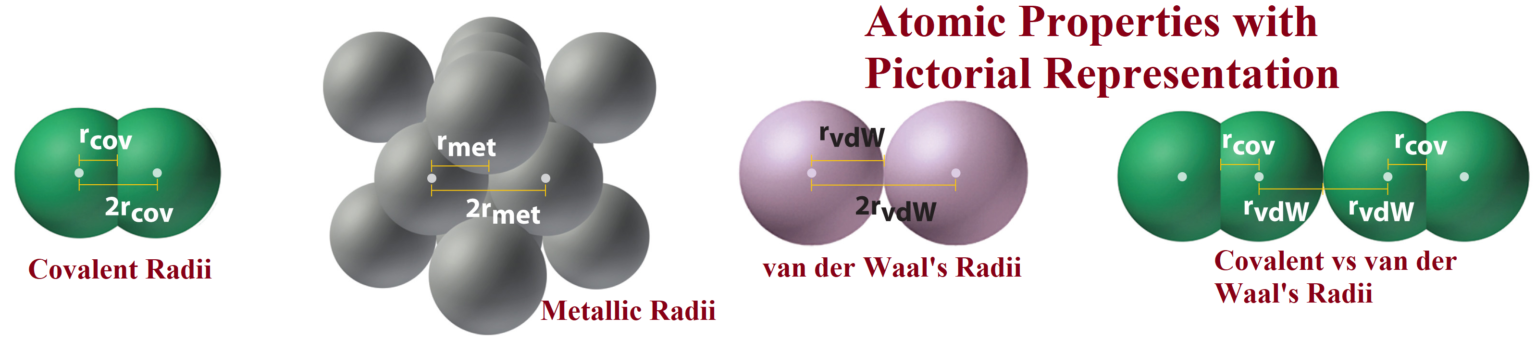
Atomic Properties with Pictorial Representation Atomic Properties with Pictorial Representation: Atomic Properties: The properties such as atomic radius, ionic radius, ionisation energy, electronegativity, electron affinity, and valence, called atomic properties. Atomic Radius: It is defined as the distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost shell containing electrons. Atomic radius is commonly expressed in picometre (pm) or angstrom (Å).it is measured by x-ray diffraction method or by spectroscopic methods. Covalent radius: One-half of the distance between the nuclei of two covalently bonded atoms of the same element in a molecule (used for non-metals). Van der Waals radius:…
Conductivity Molar conductivity and Electrolysis Resistance (R): The electrical resistance is a hindrance to the flow of electrons. Its unit is the ohm (Ω). The resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to the length of the conductor (Ɩ) and inversely proportional to the area of cross-section (A) of the conductor. R α Ɩ /A R = ρ Ɩ /A where ρ (rho) is a constant called resistivity or specific resistance. Its unit is ohm-meter (Ω m) or ohm-centimeter (Ω cm). Resistivity (ρ): It defined as the resistance offered by a conductor having unit length and unit area of…