Coordination Compounds Important Topics The concept of coordination compounds originates from the tendency for the complex formation of the transition elements. Complex compounds or coordination compounds are those molecular compounds that retain their identity in solid and in solution are known as complex compounds. K4[Fe(CN)6 ] + H2O → 4K+(aq) + [Fe(CN)6]4− (aq) Molecular or Addition Compounds: When solutions of two or more simple stable compounds in molecular proportion are allowed to evaporate, crystals of new substances, called molecular or addition compounds, are obtained. For Example: CuSO4 + 4NH3 → CuSO4·4NH3 AgCN + KCN → KCN·AgCN There are two…
Author: Dr. Vikas Jasrotia
Important Solved Questions on Mole Concept Que 1. Calculate the number of atoms of each type in 5.3 gram of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3).\ Ans 1. Given mass of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) = 5.3 g Molar mass of sodium carbonate = 23 × 2 + 12 + 16 × 3 = 106g/mol Number of moles = given mass/ Molar mass = 5.3/106 = 0.05 mol Now, 1 mole of Na2CO3 contains = 2 × 6.022 × 1023 sodium atoms ∴0.05 of Na2CO3 contains = 0.05 × 2 × 6.022 × 1023 sodium atoms = 6.022 × 1022 = 6.022 × 1022 Na atoms. 1 mol of Na2CO3 contains…
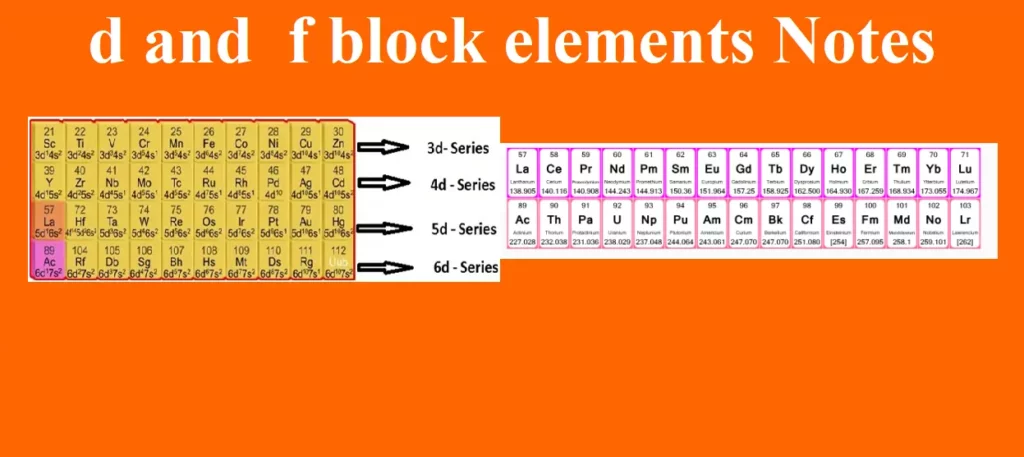
d and f block elements Notes Introduction The elements lying in the middle of the periodic table belonging to groups 3 to 12 are known as d – block elements. The elements in which the last electron enters into the d-orbitals of the penultimate shell i.e. (n–1) d where n is the last shell are called d-block elements. They are placed in between s-block and p-block elements. They show a regular transition from the highly electropositive metals of s-block elements to the less electropositive p-block elements. So, they are called transition elements. Transition elements A transition element is defined as…
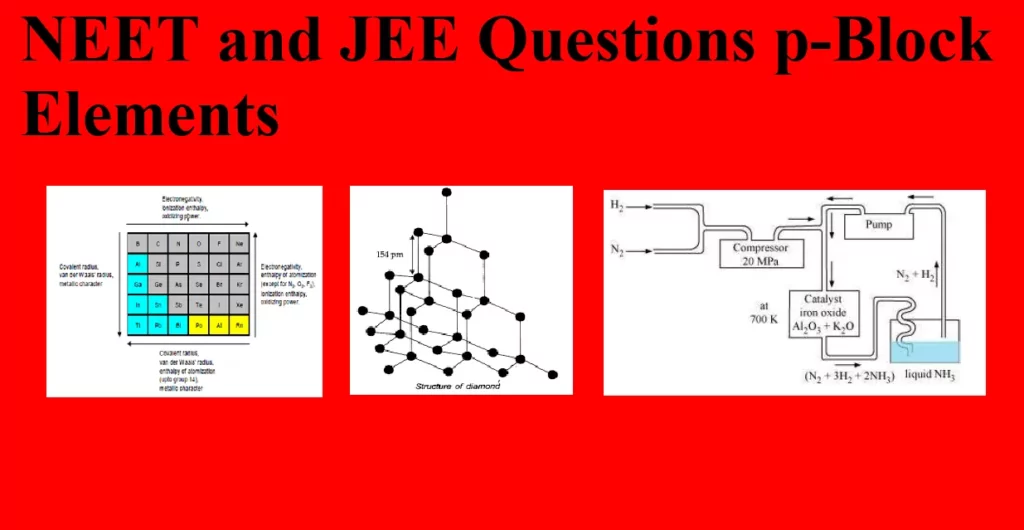
NEET and JEE Questions p-Block Elements Que 1. Which of the following elements does not form stable diatomic molecules. (a) Iodine (b) Phosphorus (c) Nitrogen (d) Oxygen Ans 1. (b) Phosphorus Explanation: Phosphorous forms tetra atomic molecule it does not form stable diatomic molecule whereas the other given elements form stable diatomic molecules(Due to larger atomic size P does not form pi bonds and so it exists as a tetra-atomic molecule in which each P atom is bonded with 3 other P atoms by 3 sigma bond. But, due to smaller atomic size N forms 1 sigma and…
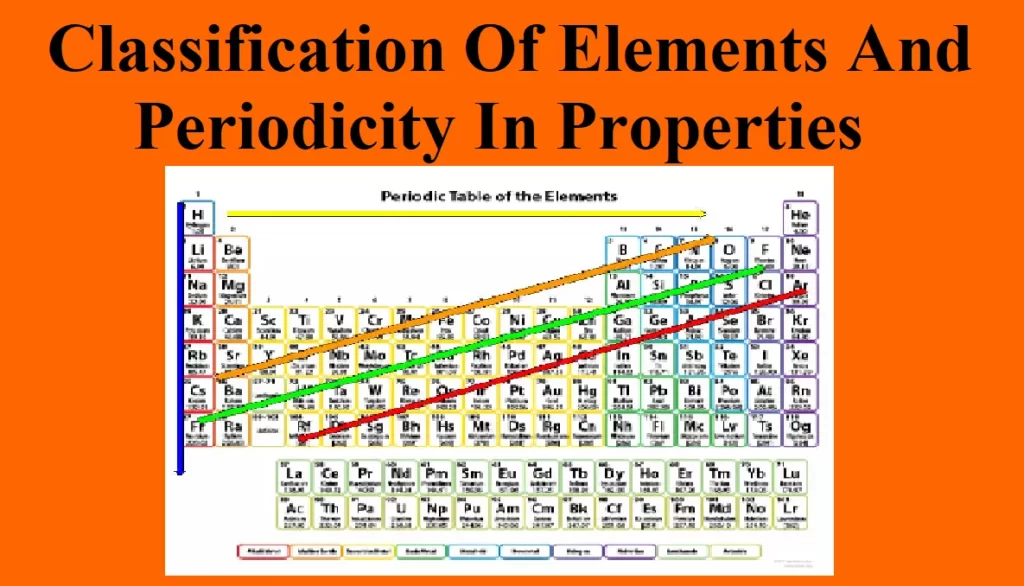
Classification Of Elements And Periodicity In Properties Classification and Blocks in Periodic Table: Topics covered: Earlier classifications Dobereiner’s Triads Newland’s law of octaves Mendeleev’s Periodic Classification Modern Periodic Table or Moseley’s Periodic Law With the discovery of a large number of elements, it became difficult to study the elements individually, so the classification of elements was done to make the study easier. Earlier Classification: Dobereiner’s Triads: In triads, the atomic mass of the middle element is approximately the average of the other two elements. This is known as the Law of Triads. This classification was applicable to very few elements…
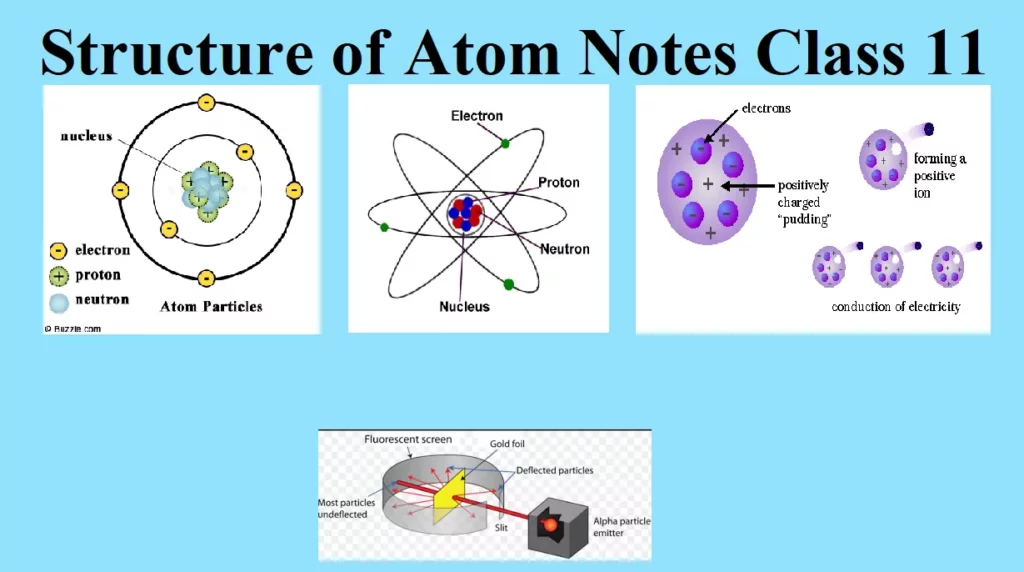
Structure of Atom Notes Class 11 STRUCTURE OF ATOM Structure of Atom The term atom was introduced by Dalton and is defined as the smallest particle of an element that retains all its properties and identity during a chemical reaction. SUB – ATOMIC PARTICLE (i) Discovery of Electron Electron was discovered by J J Thomson by Cathode ray discharge tube experiment. A cathode-ray tube is made of glass containing two thin pieces of metal (called electrodes) sealed in it. The electrical discharge through the gases could be observed only at very low pressures and at very high voltages. When…
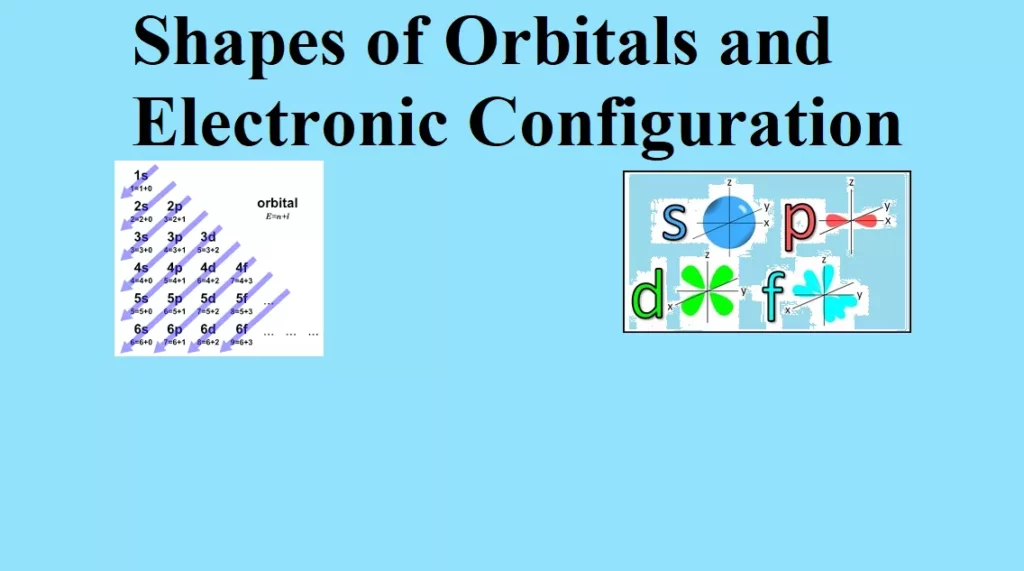
Shapes of Orbitals and Electronic Configuration Shapes of Orbitals: (i) s-orbitals: For s-orbitals, Ɩ = 0 and hence m = 0. So, there is only one possible orientation for s-orbitals. They are spherically symmetrical. The plots of probability density (ψ2) against distance from the nucleus (r) for 1s and 2s atomic orbitals are as follows: For 1s orbital, the probability density is maximum at the nucleus and it decreases with an increase in r. But for 2s orbital, the probability density first decreases sharply to zero and again starts increasing. After reaching a small maximum it decreases again and approaches zero as…
p-Block Elements Class 12 Important Questions Que 1. Sulphur has more tendency to show catenation than oxygen. Explain. Ans 1. Due to the stronger S‐S bond and due to small size and greater inter electronic repulsion O‐O bond is weakened so it can’t show catenation. Que 2. Why nitric oxide becomes brown when released into the air? Ans 2. Nitric oxide becomes brown when released into the air due to the formation of Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) 2 NO + O2 → 2 NO2 Colourless Brown Que 3. Explain why SF4 is easily hydrolysed, whereas SF6 is resistant to hydrolysis? Ans…
p-Block Elements Class 12 Notes p-Block Elements Class 12 Notes The elements in which the last electron enters in the valence p-subshell are called the p-block elements. They include elements from groups 13 to 18. Their general electronic configuration is ns2np1-6 where n = 2 (except He which has 1s2 configuration). They, includes metals, non-metals and metalloids. Elements belonging to the s and p-blocks in the periodic table are called the representative elements or main group elements. Inert pair effect: The tendency of ns2 electron pair to participate in a bond formation decreases with the increase in atomic size. Within…
Electrochemistry Class 12 Notes Syllabus:- Electrolytic cells & Galvanic cells The function of Salt Bridge Redox reaction, EMF of the cell, standard electrode potential Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) Nernst equation and its application to Chemical cell Equilibrium Constant from Nernst Equation Electrochemical Cell and Gibbs Energy Electrochemistry: It is a branch of chemistry that deals with the relationship between chemical energy and electrical energy and their interconversions. Redox Reactions: Oxidation is the process that involves the loss of electrons & reduction is a process in which it involves the gain of electrons. The reactions which involve both that reaction…