Some Basic Concepts of Organic Chemistry
Some Basic Concepts of Organic Chemistry
Que 1. Select the molecule which has only one л – bond
(a) CH2 = CH2
(b) CH2 = CHCHO
(c) CH3CH = CH2
(d) CH3CH = CHCOOH
Que 2. 2-Pentene contains
(a) 15 σ – and one л – bond
(b) 14 σ -and one л – bond
(c) 15 σ – and two л – bonds
(d) 14 σ – and two л – bonds
Que 3. Which of the following does not represent the 2 – Bromo pentane?
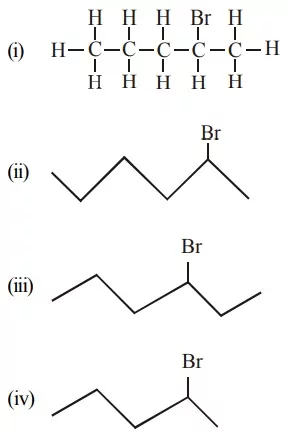
(a) (ii) and (iii)
(b) Only (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (v)
Que 4. Which of the following is incorrectly matched –
(a) Vinegar → Carboxylic acid
(b) C2H6 → Alkane
(c) Ethanol → Alcohol
(d) Methanol → Ketone
Que 5. The functional group present in organic, acid is
(a) – OH
(b) – CHO
(c) –COOH
(d) > C = O
Some Basic Concepts of Organic Chemistry
Que 6. Which of these contains the carbonyl group?
(a) Ketones
(b) Aldehydes
(c) Esters
(d) All of these
Que 7. The number of secondary hydrogens in 2, 2-dimethylbutane is
(a) 8
(b) 6
(c) 4
(d) 2
Que 8. The compound which has one isopropyl group is
(a) 2, 2, 3, 3 – Tetramethylpentane
(b) 2, 2 – Dimethylpentane
(c) 2, 2, 3- Trimethylpentane
(d) 2- Methypentane
Que 9. What is the IUPAC name of t-butyl alcohol?
(a) Butanol–2
(b) 2–Methyl-propan–2-ol
(c) Butanol–1
(d) Propanol-2
Que 10. The IUPAC name of CH3COCH (CH3)2 is –
(a) Isopropyl methyl ketone
(b) 2-methyl-3-butanone
(c) 4-methylisopropyl ketone
(d) 3-methyl-2-butanone
Que 11. What is the IUPAC name of the following compound?
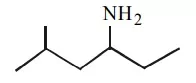
(a) 2-methyl-4-hexanamine
(b) 5-methyl-3-hexanamine
(c) 2-methyl-4-amino hexane
(d) 5-methyl-3-amino hexane
Que 12. Identify the correct IUPAC name of the compound given below
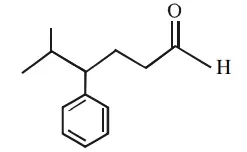
(a) 4 – benzyl – 5 – methyl hexanal
(b) 2 – methyl – 3 – phenyl hexanal
(c) 5 – isopropyl – 5 – phenyl butanal
(d) 5 – methyl – 4 – phenyl hexanal
Que 13. Which of the following is a 3-methylbutyl group?
(a) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2 –
(b) (CH3CH2)2CH –
(c) (CH3)3CCH2 –
(d) (CH3)2CHCH2CH2 –
Que 14. CH3CH2OH and CH3OCH3 are the examples of
(a) Chain isomerism
(b) Functional isomerism
(c) Position isomerism
(d) Metamerism
Que 15. The IUPAC name of the compound CH3 — CH(CH3) — CO – CH3, is
(a) 3-methyl 2-butanone
(b) 2-methyl 3-butanone
(c) isopropyl methyl ketone
(d) methyl isopropyl ketone
Some Basic Concepts of Organic Chemistry
Que 16. Methoxyethane and propanol are examples of isomerism of the type
(a) Structural
(b) Position
(c) Functional
(d) Tautomerism
Que 17. Which of the following ions is most stable?
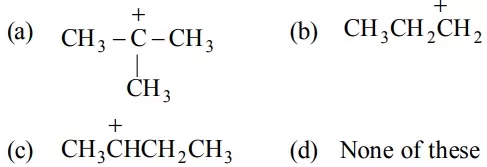
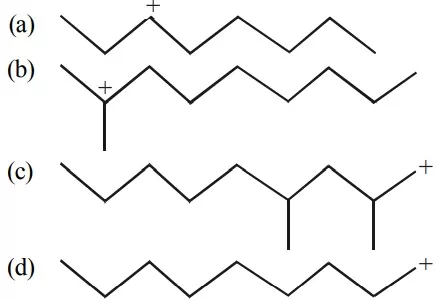
Que 18. Select the most stable carbocation amongst the following
Que 19. Heterolytic fission of C – Br bond results in the formation of
(a) free radical (b) carbanion
(c) carbocation (d) Both (b) and (c)
Que 20. What is the correct order of decreasing stability of the following cations?
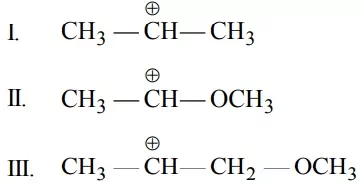
(a) II > I > III
(b) II > III > I
(c) III > I > II
(d) I > II > III
Que 21. The shape of methyl carbanion is similar to that of –
(a) BF3
(b) NH3
(c) Methyl free radical
(d)Methyl carbocation
Que 22. Which of the following is the strongest nucleophile
(a) Br–
(b) :OH–
(c) :CN–
(d) C2H5O: –
Que 23. Which of the following is an electrophile?
(a) Lewis acid
(b) Lewis base
(c) Negatively charged species
(d) None of the above
Que 24. Which of the following pairs represent electrophiles?
(a) AlCl3, H2O
(b) SO3, NO2+
(c) BF3, H2O
(d) NH3, SO3
Que 25. The increasing order of stability of the following free radicals is

Some Basic Concepts of Organic Chemistry
Que 26. Point out the incorrect statement about resonance?
(a) Resonance structures should have equal energy
(b) In resonating structures, the constituent atoms must be in the same position
(c) In resonating structures, there should not be the same number of electron pairs
(d) Resonating structures should differ only in the location of electrons around the constituent atoms
Que 27. Which of the following is an example of an elimination reaction?
(a) Chlorination of methane
(b) Dehydration of ethanol
(c) Nitration of benzene
(d) Hydroxylation of ethylene
Que 28. Which of the following is not correctly matched?
Group showing + R effect Group showing – R effect
(a) – NHCOR – COOH
(b) = C = O – OH
(c) – OR – CHO
(d) – OCOR – NO2
Que 29. The electromeric effect is a
(a) Permanent effect
(b) Temporary effect
(c) Resonance effect
(d) Inductive effect
Que 30. The kind of delocalization involving sigma bond orbitals is called
(a) Inductive effect
(b) Hyperconjugation effect
(c) Electromeric effect
(d) Mesomeric effect
Que 31. Hyperconjugation is most useful for stabilizing which of the following carbocations?
(a) neo-Pentyl
(b) tert-Butyl
(c) iso-Propyl
(d) Ethyl
Que 32. Which out of A, B, C, and D is/are not correctly categorized.
| Nucleophile | Electrophile | |
| A | HS– | Cl+ |
| B | BF3 | (CH3)3 N |
| C | H2N– | -C=O |
| D | R3C-X | C2H5O– |
| X – Halogen |
(a) B, C and D
(b) C and D
(c) C only
(d) B and D
Que 33. The IUPAC name of the following compound is
(CH3)2CH – CH2CH = CH – CH = CH – CH (CH3)C2H5
(a) 1,1,7,7-tetramethyl-2,5-octadiene
(b) 2,8-dimethyl-3,6-decadiene
(c) 1,5-di-iso-propyl-1,4-hexadiene
(d) 2,8-dimethyl-4,6-decadiene
Que 34. The least number of carbon atoms in alkane showing isomerism is
(a) 3
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 4
Que 35. The organic reaction which proceeds through heterolytic bond cleavage is called ________
(a) Ionic
(b) Polar
(c) Nonpolar
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Some Basic Concepts of Organic Chemistry



