Coordination Compounds Class 12 NCERT Solutions – Intext
Coordination Compounds Class 12 NCERT Solutions
Que 9.1: Write the formulas for the following coordination compounds:
(i) Tetraamminediaquacobalt(III) chloride
(ii) Potassium tetracyanonickelate(II)
(iii) Tris(ethane−1,2−diamine) chromium(III) chloride
(iv) Amminebromidochloridonitrito-N-platinate(II)
(v) Dichloridobis(ethane−1,2−diamine)platinum(IV) nitrate
(vi) Iron(III) hexacyanoferrate(II)
Ans 9.1: (i) [Co (H2O) (NH3)4] Cl3
(ii) K2 [Ni (CN)4]
(iii) [Cr (en)3] Cl3
(iv) [Pt (NH3) Br Cl (NO2)]–
(v) [Pt Cl2 (en)2] (NO3)2
(vi) Fe4 [Fe (CN)6]3
Que 9.2: Write the IUPAC names of the following coordination compounds:
(i) [Co (NH3)6] Cl3
(ii) [Co (NH3)5 Cl] Cl2
(iii) K3 [Fe (CN)6]
iv) K3 [Fe (C2O4)3]
(v) K2 [Pd Cl4]
(vi) [Pt (NH3)2 Cl (NH2CH3)] Cl
Ans 9.2: (i) Hexaamminecobalt(III) chloride
(ii) Pentaamminechloridocobalt(III) chloride
(iii) Potassium hexacyanoferrate(III)
(iv) Potassium trioxalatoferrate(III)
(v) Potassium tetrachloridopalladate(II)
(vi) Diamminechlorido(methylamine)platinum(II) chloride
Que 9.3: Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complexes and draw the structures for these isomers:
i. K [Cr (H2O)2 (C2O4)2]
ii. [Co (en)3] Cl3
iii. [Co (NH3)5 (NO2)] (NO3)2
iv. [Pt (NH3) (H2O) Cl2]
Ans 9.3:

Que 9.4: Give evidence that [Co (NH3)5 Cl] SO4 and [Co (NH3)5 SO4] Cl are ionization isomers.
Ans 9.4: When ionization isomers are dissolved in water, they ionize to give different ions. These ions then react differently with different reagents to give different products.
[Co (NH3)5 Cl] SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4↓
White precipitate
[Co (NH3)5 Cl] SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4↓
White precipitate
[Co (NH3)5 Cl] SO4(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → No reaction
[Co (NH3)5 Cl] SO4(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → No reaction
[Co (NH3)5 SO4] Cl(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → No reaction
[Co (NH3)5 SO4] Cl(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → No reaction
[Co (NH3)5 SO4] Cl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → AgCl↓
White precipitate
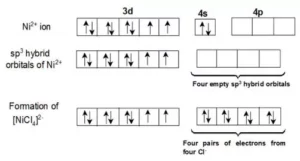
Que 9.5: Explain on the basis of valence bond theory that [Ni(CN)4]2− ion with square planar structure is diamagnetic and [NiCl4] 2− ion with tetrahedral geometry is paramagnetic.
Ans 9.5: Outer electronic configuration of nickel (Z = 28) in-ground state is 3d84s2. Nickel in this complex is in a + 2 oxidation state. It achieves + 2 oxidation state by the loss of the two 4s-electrons. The resulting Ni2+ ion has an outer electronic configuration of 3d8.
There are 4 CN− ions. Thus, it can either have a tetrahedral geometry or square planar geometry. Since CN− ion is a strong field ligand, it causes the pairing of unpaired 3d electrons.
It now undergoes dsp2 hybridization. Since all electrons are paired, it is diamagnetic.

In the case of [NiCl4]2−, Cl− ion is a weak field ligand. Therefore, it does not lead to the pairing of unpaired 3d electrons. Therefore, it undergoes sp3 hybridization. Since there are 2 unpaired electrons, in this case, it is paramagnetic in nature.
Que 9.6: [NiCl4]2− is paramagnetic while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic though both are tetrahedral. Why?
Ans 9.6: As we can see in the question, there are 4 ligands in the compound which means it is a tetrahedral complex.
Since, Cl− is a strong field ligand and it will not cause the pairing of the 3d electrons. This will lead to sp3 hybridization. It is given below:
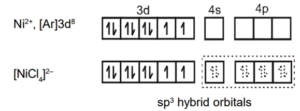
As two unpaired electrons are present, it is paramagnetic.
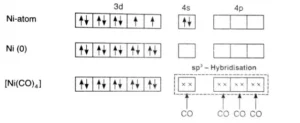
In [Ni(CO)4], Ni is in the zero oxidation state i.e., it has a configuration of 3d8 4s2.
But CO is a strong field ligand. Therefore, it causes the pairing of unpaired 3d electrons. Also, it causes the 4s electrons to shift to the 3d orbital, thereby giving rise to sp3 hybridization. Since no unpaired electrons are present in this case, [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic.
Que 9.7: [Fe (H2O)6]3+ is strongly paramagnetic whereas [Fe (CN)6]3− is weakly paramagnetic. Explain.
Ans 9.7: In the given complexes, Fe is the central metal ion and in both cases, the oxidation state of Fe is +3. Therefore, it will be in d5 configuration.
Since CN− is a strong field ligand, it causes unpaired electrons to be paired. There is just one unpaired electron in the d-orbital thus remaining.

Coordination Compounds Class 12 NCERT Solutions
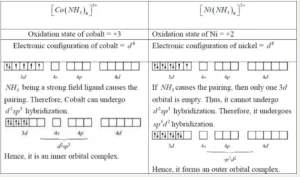
Que 9.8: Explain [Co(NH3)6]3+ is an inner orbital complex whereas [Ni(NH3)6]2+ is an outer orbital complex.
Ans 9.8: In [Co (NH3)6]3+ Co is in +3 state and has configuration 3d6. In the presence of NH3, 3d electrons pair up leaving two d-orbitals empty. Hence, the hybridization is d2sp3 forming an inner orbital complex. In [Ni (NH3)6]2+, Ni is in a +2 state and has configuration 3d8. In presence of NH3, the 3d electrons do not pair up. The hybridization is sp3d2 forming an outer orbital.
Que 9.9: Predict the number of unpaired electrons in the square planar [Pt (CN)4]2− ion.
Ans 9.9: In this complex, Pt is in the +2 state. It forms a square planar structure. This means that it undergoes dsp2 hybridization. Now, the electronic configuration of Pd+2 is 5d8. CN – being a strong field ligand causes the pairing of unpaired electrons. Hence, there are no unpaired electrons in [Pt(CN)4]2-.

Que 9.10: The hexaquomanganese(II) ion contains five unpaired electrons, while the hexacyanoion contains only one unpaired electron. Explain using Crystal Field Theory.
Ans 9.10: Mn(II) ion has 3d5 configuration. In the presence of H2O molecules acting as weak field ligands, the distribution of these five electrons is t32ge2 i.e., all the electrons remain unpaired to form a high spin complex. However, in the presence of CN– acting as strong field ligands, the distribution of these electrons is t52ge0g i.e., two t2g orbitals contain paired electrons while the third t2g orbital contains one unpaired electron. The complex formed is a low spin complex.
Que 9.11: Calculate the overall complex dissociation equilibrium constant for the [Cu (NH3)42+] ion, given that β4 for this complex is 2.1 × 1013.
Ans 9.11: Overall stability constant (β4) = 2.1 × 1013.
Thus, the overall dissociation constant is
= 1/ β4 = 1/2.1 × 1013 = 4.7 × 10-14
Coordination Compounds Class 12 NCERT Solutions
Coordination Compounds Class 12 Notes



