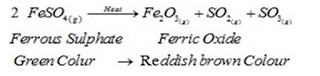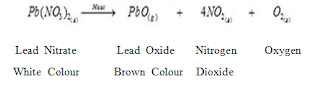Combination, Decomposition, Displacement And Double Displacement reactions
Types of Chemical Reactions:
i). Combination Reaction
ii). Decomposition Reaction
a). Thermal Decomposition
b). Electrolytic Decomposition
iii). Displacement Reaction OR Substitution reaction
iv). Double Displacement Reaction
a). Precipitation Reaction
b). Neutralisation Reaction
v). Redox Reaction
vi). Oxidation Reaction
vii). Reduction Reaction
viii). Endothermic Reaction
ix). Exothermic Reaction
Explanation of the types of Chemical reactions i.e Combination, Decomposition, Displacement And Double Displacement reactions using examples:
i). Combination Reaction:
The reactions in which two or more substances combine to form a new substance are called combination reactions. For example:
a). 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) → 2 MgO
Magnesium Oxygen Magnesium oxide (White ash)
(basic) turns red litmus blue
b). In the laboratory, iron sulphide is prepared by mixing iron and sulphur.
Fe(s) + S(s) → FeS(s)
c). Burning of carbon monoxide in oxygen to form carbon dioxide.
2CO (g) + O2(g) → 2CO2 (g)
d). Calcium oxide upon reaction with water produces calcium hydroxide.
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
Calcium Oxide Water Calcium Hydroxide
(Quick Lime) (Slaked Lime)
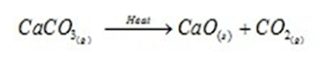
ii). Decomposition reactions:
These are opposite to combination reactions. A single compound decomposes or break down to give two or more simpler substances.
It is of following types:
i).Thermal Decomposition:
When a decomposition reaction is carried out by heating.
For Example:
-
Mercuric oxide, when heated, undergoes thermal decomposition, to give mercury and oxygen

iii). Displacement Reaction OR Substitution reaction:
A more reactive element (metal) displaces less reactive element (metal) from its aqueous salt soln. For example:
-
Zn (s) + FeSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Fe (s)
(green) (Colourless)
-
Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s) ↓
Iron Blue Green Reddish Brown
-
Mg (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → MgSO4 (aq) + H2O (g)
Magnesium Sulphuric Magnesium Water
Acid Sulphate
-
Cu (s) + 2AgNO3 (aq) → Cu (NO3)2 (aq) + 2Ag (s).
Copper Silver Nitrate Copper Nitrate Silver
-
KI (aq) + Cl2 (g) → KCl (aq) + I2 (g)
Potassium Chlorine Potassium Iodine
Iodide Chloride
iv). Double Displacement Reaction:
The chemical reactions in which compounds react to form two different compounds by mutual exchange of ions are called double displacement reactions.
Reactions occurs by two different ways
a). Precipitation: In such reactions due to exchange of ions some insoluble material is formed. This insoluble material is called precipitate and the reaction is called precipitation reaction. For example:
-
ZnSO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → ZnCl2 (aq) + BaSO4 (s)
Zinc Barium Zinc Barium
Sulphate Chloride Chloride Sulphate (White)
-
2 HCl (aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) → 2 HNO3 (aq) + PbCl2 (s) ↓
Hydrochloric Lead Nitric Lead (White)
Acid Nitrate Acid Chloride
-
Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2 KI (aq) → PbI2 (aq) ↓ + KNO3 (s)
Lead Potassium lead Potassium
Nitrate Iodide Iodide Nitrate
b) Neutralization Reaction: In this type of reaction an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water by exchange of ions.
-
NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O
Sodium Hydrochloric Sodium Water
Hydroxide Acid Chloride
(Base) (Acid) (Salt) (Water)
-
ZnO + HNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + H2O
Zinc Nitric Zinc Water
Oxide Acid Nitrate
All these types of Combination, Decomposition, Displacement and Double Displacement reactions are explained using examples along with the colour change that takes place during reactions.