Redox Reaction, Oxidation and Reduction Reactions with exact equations
This part of the types of chemical reaction of chapter Chemical Reactions and Equations involve the types Redox Reaction, Oxidation and Reduction Reactions with exact equations.
v). Redox Reaction: A reaction in which reduction and oxidation takes place simultaneously.
- ZnO (s) + C (s) → Zn (s) + CO (g)
Zinc Carbon Zinc Carbon
Oxide Monoxide
vi). Oxidation Reaction: Oxidation is the gain of oxygen. For example:
- 2 Cu (s) + O2 (g) → 2 CuO (s) (Black)
Copper Oxygen Copper Oxide
- 2 Mg(s) + O2 (g) → 2MgO (s)
Magnesium Oxygen Magnesium Oxide
OR
Removal of hydrogen is also oxidation. For Example:
- 2HI (g) → H2 (g) + I2 (g)
Hydrogen Hydrogen Iodine
Iodic Acid
VII). Reduction Reaction: Reduction is the gain of hydrogen. For example:
- H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2 HCl
Hydrogen Chlorine Hydrochloric Acid
OR
Removal of oxygen is also reduction. Foe Example:
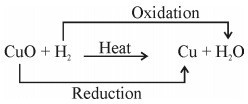
- CuO (s) + CO (g) → Cu (s) + CO2 (g)
Copper Oxide Carbon Copper Carbon Dioxide
(Black) Monoxide (Reddish Brown)
- ZnO (s) + C (s) → Zn (s) + CO (g)
Zinc Carbon Zinc Carbon
Oxide Monoxide
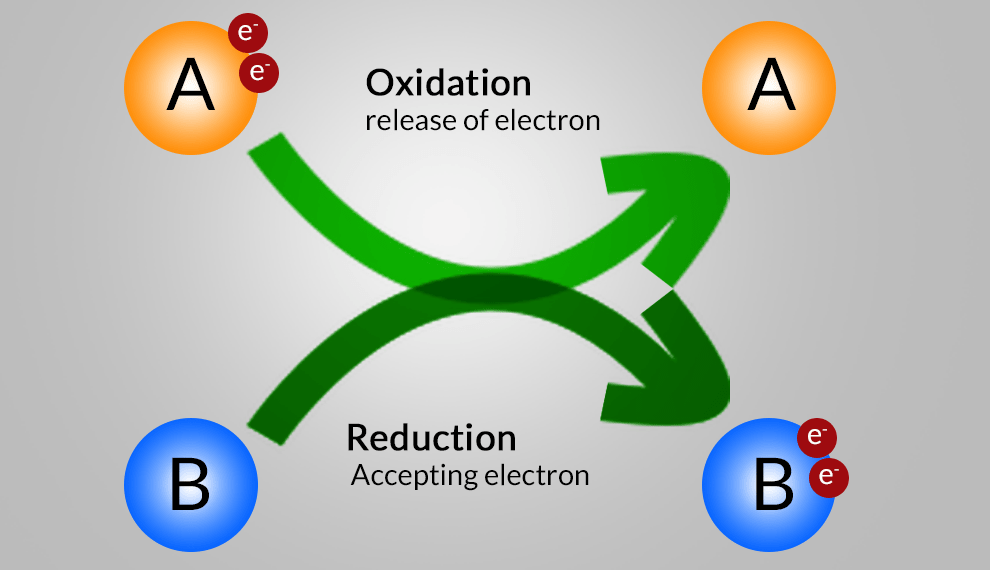
An oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction is a type of chemical reaction that involves a transfer of electrons between two species. An oxidation-reduction reaction is any chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of a molecule, atom, or ion changes by gaining or losing an electron. Redox Reaction, Oxidation and Reduction Reactions with exact equations are common and vital to some of the basic functions of life, including photosynthesis, respiration, combustion, and corrosion or rusting.
- Oxidation: The process in which there is loss of electrons.
- Reduction: The process in which there is gain of electrons.
- Oxidizing Agent: A substance that brings about oxidation.
- Reducing Agents: A substance that brings about reduction.
viii). Endothermic Reactions: Reaction in which heat is absorbed to carry out the chemical reaction. For Example:
- CaCO3 (s) + Heat → CaO (s) + CO2 (g) Calcium Calcium Carbon
Carbonate Oxide Dioxide
- C(s) + H2 O (s) + Heat → CO (g) + H2 (g)
Carbon Carbon
Monoxide (Evolve)
ix). Exothermic Reactions: Reaction in which heat is evolved during the chemical reaction. For Example:
- C + O2 → CO2 (g) + heat