Normality and Molarity
NORMALITY: Normality is one way to express the concentration of the solution
It is the number of gram equivalents of a solute present in one litre of solution.
 w = Mass of solute in gram
w = Mass of solute in gram
V = Volume of solution in ml
E = Equivalent weight of solute
The equivalent weight of Solute: It is the number of parts by weight of the substance that combines or displaces, directly or indirectly, 1.008 parts by mass of hydrogen or 8 parts by mass of oxygen, or 35.5 parts by mass of chlorine. It can be calculated as
(i) Equivalent mass for elements = Atomic mass / Valency
(ii) Equivalent mass for acids = Molecular mass / Basicity of acids
(iii) Equivalent mass for bases = Molecular mass / Acidity of base
(iv) Equivalent mass for salts = Formula mass / (Valency of cation) (No. of cations)
(v) Equivalent mass for oxidising agents = Formula Mass / No. of electrons gained per molecule
vii) Equivalent weight of radicals = Formula mass of radical / No. of units of charge
On dilution of the solution, the number of equivalents of the solute is conserved, and thus, we can apply the formula: N1V1 = N2V2
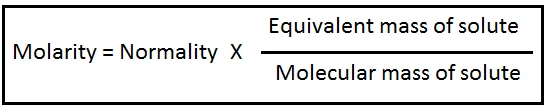
Relation between Normality and Molarity: