Assertion Reason Type Questions Class 11 – Chapter Chemical Equilibrium
Assertion Reason Type Questions Class 11
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If the assertion is true but the reason is false.
(d) If the assertion is false but the reason is true.
1. Assertion: The equilibrium constant is fixed and is the characteristic of any given chemical reaction at a specified temperature.
Reason: The composition of the final equilibrium mixture at a particular temperature depends upon the starting amount of reactants.
Ans 1. C
2. Assertion: The endothermic reactions are favoured at lower temperatures and the exothermic reactions are favoured at a higher temperature.
Reason: when a system in equilibrium is disturbed by changing the temperature, it will tend to adjust itself so as to overcome the effect of change.
Ans 2. D
3. Assertion: A catalyst does not influence the values of the equilibrium constant.
Reason: Catalysts influence the rate of both forward and backward reactions equally.
Ans 3. A
4. Assertion: Kp = Kc for all reactions.
Reason: At constant temperature, the pressure of the gas is proportional to its concentration.
Ans 4. D
5. Assertion: The melting point of ice decreases with the increase in pressure.
Reason: Ice contracts on melting.
Ans 5. A
6. Assertion: In dynamic equilibrium, forward and backward reactions continue to take place with equal rates.
Reason: In dynamic equilibrium, colour and density change with time.
Ans 6. C
7. Assertion: The equilibrium constant for the reaction. CaSO4. 5H2O (s) ⇌ CaSO4. 3H2O (s) + 2H2O (g) is
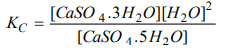
Reason: Equilibrium constant is the ratio of the product of the molar concentration of the substances produced to the product of the molar concentrations of reactants with each concentrations term raised to the power equal to the respective stoichiometric constant.
Ans 7. D
8. Assertion: The gas-phase reaction PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ PCl5(g) shifts to the right on increasing pressure.
Reason: When pressure increase, equilibrium shifts towards more number of moles.
Ans 8. C
9. Assertion: N2 + 3 H2 ⇌ NH3; ∆H = –92 kJ. High pressure favours the formation of ammonia.
Reason: An increase of external pressure on the above reaction at equilibrium favours the reaction in the direction in which the number of moles decreases.
Ans 9. A
10. Assertion: If Qc (reaction quotient) < KC (equilibrium constant) reaction moves in direction of reactants.
Reason: The reaction quotient is defined in the same way as the equilibrium constant at any stage of the reaction.
Ans 10. D
11. Assertion: The physical equilibrium is not static but dynamic in nature.
Reason: The physical equilibrium is a state in which two opposing processes are proceeding at the same rate.
Ans 11. A
12. Assertion: Kp = Kc for all reactions.
Reason: At constant temperature, the pressure of the gas is proportional to its concentration.
Ans 12: D
13. Assertion: NaCl solution can be purified by the passage of hydrogen chloride through the brine.
Reason: his type of purification is based on Le-Chatelier’s principle.
Ans 13. C
14. Assertion: If water is heated to 59°C, the pH will increase.
Reason: Kw increases with an increase in temperature.
Ans 14: D
15. Assertion: Ice melts slowly at higher altitudes.
Reason: The melting of ice is favoured at high pressure because ice → water shows a decrease in volume.
Ans 15. A
16. Assertion: According to Le-Chatelier’s principle addition of heat to an equilibrium solid ⇌ liquid results in a decrease in the amount of solid.
Reason: Reaction is endothermic, so on heating forward reaction is favoured.
Ans 16. B
17. Assertion: The addition of HCl(aq.) to CH3COOH (aq.) decrease the ionisation of CH3COOH (aq.).
Reason: Due to the common ion effect H+, ionisation of CH3COOH decreases.
Ans 17. A
18. Assertion: The equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction is the inverse of the equilibrium constant for the reaction in the forwarding direction.
Reason: Equilibrium constant depends upon the way in which the reaction is written.
Ans 18. A
19. Assertion: Equilibrium constant has meaning only when the corresponding balanced chemical equation is given.
Reason: Its value changes for the new equation obtained by multiplying or dividing the original equation by a number.
Ans 19. A
20. Assertion: The ionisation constants of weak diprotic acid are in the order of Ka1 > Ka2.
Reason: Removal of H+ from anion is difficult as compared to neutral atom.
Ans 20: A
Assertion Reason Type Questions Class 11



