Valence Bond Theory Coordination Compounds
Valence Bond Theory
The bonding in coordination compounds can be explained by Valence Bond Theory (VBT). It was developed by Pauling. This theory mainly deals with the electronic structure of central metal ion, geometry, magnetic properties of complex, kind of bonding. According to this theory, the metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands form inner orbital and outer orbital complex. These hybridized orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals that can donate electron pairs for bonding.
The main features of the valence bond theory are summarized below:
1. Inner orbital complex: When the complex formed involved inner (n-1)d orbitals for hybridisation (d2sp3 ). Electrons are made to pair up so complex will be either diamagnetic or has fewer unpaired electrons. It is a low spin complex. Eg. [V(H2O)6]3+, [Co(NH3)6]3+.
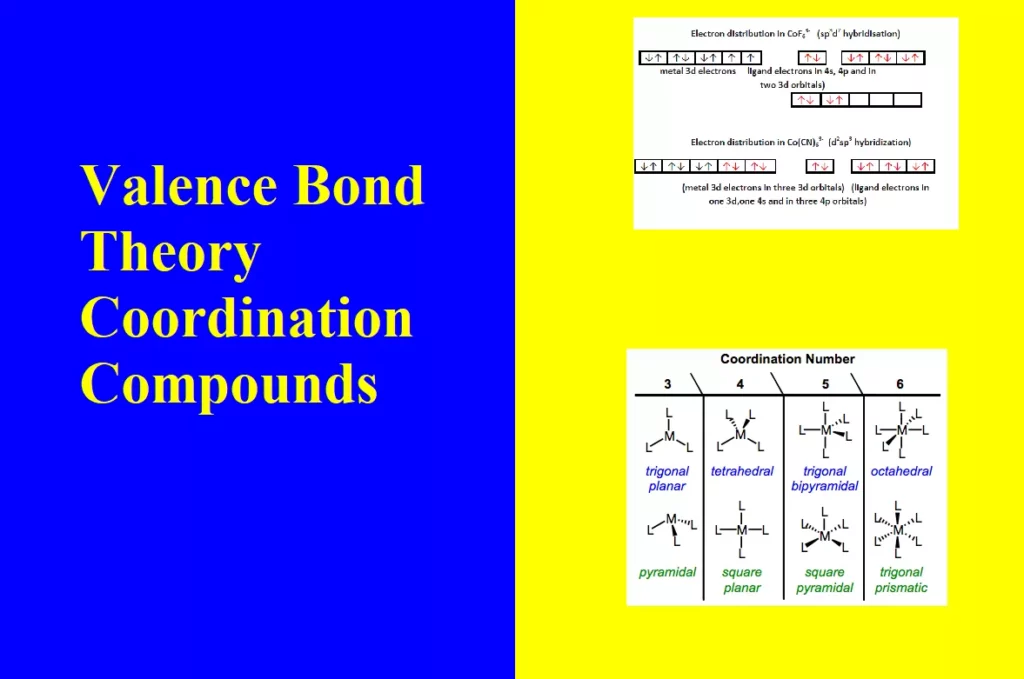
2. Outer orbital complex: When the complex formed uses outer d orbitals for hybridisation, (sp3d2), it has a large number of unpaired electrons. It is a high spin complex. Eg. [CoF6]3-, [Fe(H2O)6]3+.

FORMATION OF OCTAHEDRAL COMPLEXES
Example: Inner orbital complex, [Co(NH3)6]3+
Co→ [Ar]3d74s2
Co+3→ [Ar]3d64s0
With a +3 oxidation state NH3 act as a strong ligand.
All electrons are paired therefore, complex will be diamagnetic in nature.

Example: Inner orbital complex, [Fe(CN)6]3-
Fe → [Ar]3d64s2
Fe+3→ [Ar]3d54s0
With +3 oxidation state CN act as a strong ligand.

Valence Bond Theory Coordination Compounds
FORMATION OF SQUARE PLANAR COMPLEXES
Example: Inner orbital complex, [Ni(CN)4]2-:
Ni – 3d8, 4s2
Ni2+ – 3d8, 4s0

FORMATION OF TETRAHEDRAL COMPLEXES
Example: Inner orbital complex [Ni(CO)4]:

Outer orbital complexes
i). In these complexes s, p, and d orbitals which are involved in hybridization, belong to the highest quantum number (n).
ii) Complex compound formed by the use of outer n and d orbitals will be paramagnetic.
iii) Outer orbital complexes are also known as high-spin or spin-free complexes.
iv). The outer orbital complexes have a high number of unpaired electrons, E.g. [CoF6]3–
For Example: Outer orbital complex [CoF6]3–

For Example: Outer orbital complex [Cr(H2O)6]3+:

Valence Bond Theory Coordination Compounds
Limitations of Valence Bond Theory:
Even though the valence bond theory explains the formation, structures, and magnetic behavior of coordination compounds to a larger extent, it suffers from the following shortcomings:
i). It does not explain the relative energies of different structures.
ii). It offers no explanation of the colour observed for the complexion.
iii). It cannot predict whether a 4-coordinate complex will be tetrahedral or square planar.
iv). It does not take into account the splitting of d-energy levels. v. It does not explain the spectra of complexes.
Valence Bond Theory Coordination Compounds