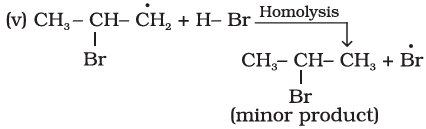Haloalkanes And Haloarenes
Read the given passage and answer the questions below:
Passage – 1:
Alkyl Halides can be readily prepared from Alkenes by addition reactions with Hydrogen Halides. When the alkene is symmetrical about the double bond, only one product is obtained. But if the alkene is unsymmetrical, the addition of Hydrogen Bromide results in the formation of two products. The addition of HBr to an unsymmetrical alkene in the presence of an organic peroxide also results in the formation of two products. The only difference is in the quantities of isomeric bromides obtained in each case, since the mechanism is different.
Que 1. What is the major product obtained when Propene reacts with HBr? What rule governs the formation of this product?
Ans 1. 2-Bromopropane. Rule Governed – Markovnikov’s Rule
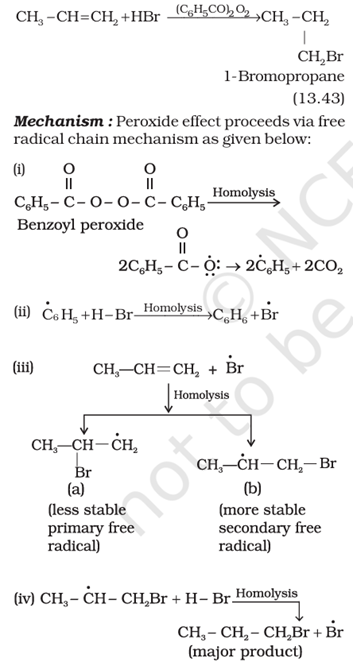
Que 2. What mechanism is adopted in the presence of Benzoyl Peroxide?
Ans 2. Free Radical Electrophilic addition.
Que 3. Why does only HBr show these anomalies, unlike HI or HCl?
Ans 3. Because HCl has a high bond dissociation enthalpy. I- produced during the reaction oxidises to I2.
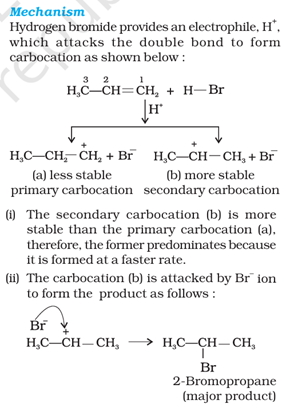
Que 4. Write the mechanism of the addition reaction of Propene with HBr in the presence or in the absence of organic peroxides.
Ans 4. Mechanism of Markovnikov Rule:
Anti Markovnikov Rule:
Haloalkanes And Haloarenes
Passage 2-
The substitution reaction of alkyl halides occurs in SN1 or SN2 mechanism. Whatever mechanism alkyl halide follows for the substitution reaction to occur, the polarity of the carbon-halogen bond is responsible for the substitution reaction. The rate of SN1 reactions are governed by the stability of carbocation, whereas for SN2 reactions steric factor is the deciding factor. If the starting material is a chiral compound, we may end up with an inverted product or a racemic mixture, depending upon the type of mechanism followed by the alkyl halide. Cleavage of ethers with HI is also governed by the steric factor and the stability of carbocation, which indicates that in organic chemistry, these two major factors help us in deciding the kind of product formed.
Que 1. Predict the stereochemistry of the product formed if an optically active alkyl halide undergoes a substitution reaction by SN1 mechanism.
Ans 1. A racemic mixture will be formed.
Que 2. Name the instrument used for measuring the angle by which the plane-polarised light is rotated.
Ans 2. Polarimeter
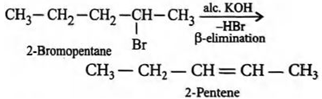
Que 3. Predict the major product formed when 2-bromopentane reacts with alcoholic KOH.
Ans 3. Pent-2-ene will be the major product.
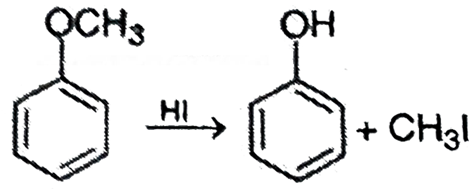
Que 4. Write the structure of the products formed when anisole is treated with HI.
Ans 4. Phenol and CH3I are formed.
Haloalkanes And Haloarenes